What is CAP Theorem and the significance of it in distributed systems?
What is CAP Theorem and the significance of it in distributed systems?
CAP Theorem was proposed by Eric Brewer in the context of distributed systems or web service. A web service is implemented by set of servers distributed over distant data centers.
CAP Theorem was introduced as a trade-off between consistency, availability and partition tolerance.
Consistency means you can write and everyone sees the write or every successful read request receives the most recent write request.
Availability means every request receives a non-error response,
Partition tolerance means continue to operate despite an arbitrary number of messages being dropped by the network between the nodes due to network partition.
Proof of CAP Theorem
Let’s imagine a distributed system with 2 nodes and let’s see how Brewer proved the CAP Theorem with the below example.
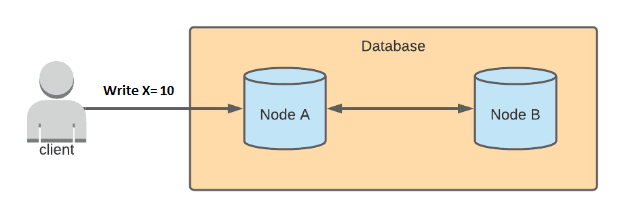
Consider user writing X to 10 into both these nodes A and B, since there is a network partition involved both A and B can’t see the update immediately. If write goes to Node A, Node B can’t see the write. Now Node B is inconsistent but available. Now we see we can’t have Consistency property doesn’t hold True.
Lets say now we switch off Node B, now the data is written to A and always be consistent and have partition tolerance. Now Availability goes to toss as we are dependent on one node.
Trade-off’s
Let us try to forfeit each one of the properties and see an example and use case for each case.
| Forfeit Partitions | Forfeit Availability | Forfeit Consistency | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|
| Definition | In this the case the data reside on one Machine and Consistency and Availability (CA) are given priority. | In this the case the data reside on multiple clusters Consistency and Partition tolerance (CP) are given priority | In this the case the data reside on multiple machines and Consistency and Partition tolerance (AP) are given priority |
| Real world Use case | Imagine a banking application where users can check their account balances, transfer funds and withdraw money from ATM. In this scenario, the bank values data consistency and ensure every user sees the most up-to-date account balances. | Imagine an Amazon app, where 2 customers are attempting to buy an app simultaneously and there is only 1 item left and the customers are attempting to complete the payment. In this case if one gets and other doesn’t get the product the company has refund for one of the customers and it would have lost trust. In this case it would be better to choose CP database. | Imagine a use case where an eCommerce service provider maintains product prices of millions of products. Let’s says there is a need to update all the price due to some tax changes. The update to all the products across multiple nodes may take long time. There may be a down time because of this. Or another option for the Company to reduce downtime is to choose Availability over Consistency. Here there may be inconsistency in product prices. But it can correct it last stage or cancel the order and refund the money if the tax wasn’t updated. |
| Example | Single site databases like MYSQL, Postgres | Redis, Memcached, HBase and MongoDB | Cassandra, Dynamo, CouchDB, Elastic search. |
Reference:
Towards Distributed Systems – PODC KeyNote July 2000 - Eric A Brewer Link: https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~brewer/cs262b-2004/PODC-keynote.pdf
Perspectives on the CAP Theorem – Seth Gilbert, Nancy A Lynch Link: http://groups.csail.mit.edu/tds/papers/Gilbert/Brewer2.pdf
